Busbar System Design, Construction and Implementation for Industrial Control Panel Installations
Often overlooked as a power distribution option in industrial control panels, busbars offer an impressive combination of cost-effectiveness, safety, space savings and adaptability.
By: Klaus Tum – Product Director at Altech Corp.
Modern industrial operations are increasingly turning to busbars to effectively distribute power in control panels — and for good reason. With a host of benefits like cost-effectiveness, safety and space savings, today’s busbars outmatch more prevalent power distribution methods that typically involve complex wiring arrangements or trunking.
Like the operations that are adopting them, busbars also need to be flexible and adaptable to changing production requirements and equipment installations. Whether you’re planning to integrate a busbar for your manufacturing operation, data center, warehouse, hospital or power plant, there are several important factors to consider as you design and build an appropriate busbar system.
This article will provide an overview of some of the advantages and key design fundamentals for busbar systems, along with important regulatory compliance considerations and implementation strategies.
An Attractive Choice for Industrial Control Panels
A busbar system offers several benefits versus traditional cabling and terminal blocks for power distribution in industrial control panels, particularly when it comes to cost advantages and safety. Here’s why:
- Cost-effectiveness: Busbars have a low-impedance design that keeps resistance and energy losses low, resulting in more efficient use of the generated power and, accordingly, reduced operating costs. Their robust construction protects against physical and environmental damage for long service life with less inspection and repairs. And, since busbars systems do not rely on large cables or their unwieldy arrangements, they offer material savings, as well as easier installation and access by personnel for maintenance and troubleshooting. Collectively, these advantages offer a lower total cost of ownership and a long system lifetime.
- Safety: Implementers can expect greater peace of mind from busbar systems because they do not involve complex cabling and their associated fault risks. Their “touch” safe design includes insulated and covered components that protect against accidental contact with live parts, as well as electric shocks and arc flashes. They also must meet stringent safety standards put in place by agencies like Underwriters Laboratories (UL), Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), the European Committee for Standardization (CEN) and others.
Busbar System Fundamentals: Materials
- Conductors: Effective power distribution starts with an appropriate conductive material. Copper and aluminum are commonly used for busbar conductors and are known for their ability to efficiently conduct and distribute electricity across circuits. If an application calls for a lightweight busbar, aluminum is a sensible choice. Otherwise, copper offers excellent conductivity (59.6 S/m at 20°C), has exceptional mechanical strength and is less susceptible to stressors like vibrations and damaging impacts. These factors, along with low energy losses, make copper a robust and reliable busbar material that doesn’t burden implementers with frequent downtime for replacement and maintenance.
In addition to having excellent mechanical strength, copper is also preferred due to its flexibility under challenging conditions like fluctuating temperatures and vibrations. In high-current or high-heat applications, solid copper exhibits excellent thermal conductivity with a lower coefficient of thermal expansion. Joints remain stable during current or thermal cycling, while conventional cable connections are susceptible to loosening. Taken together, copper busbars exhibit greater structural integrity with little degradation and longer lifespans for key components.
- Insulation: While your conductor material may be the first thought that comes to mind when selecting a busbar, safety must also be among your top priorities. Accordingly, you should select your insulator with safety in mind. Among your options, polyamide (PA), also known as nylon, boasts exceptional insulating capabilities and short circuit prevention, high thermal stability across a wide temperature range, good resistance to various chemicals, high strength and durability, space savings versus cables of the same capacity and excellent heat dissipation thanks to its high dielectric resistance. Polyamide may not be desirable in sunlight- or moisture-intensive environments, however.
Busbar System Fundamentals: Key Design Criteria
Simply put, a busbar’s cross sectional area is the most important aspect of its design. After all, this figure affects not only the busbar’s actual current-carrying capacity, or ampacity, it also influences thermal characteristics, efficiency and reliability. Busbars with a larger cross section have low electrical resistance and therefore are able to dissipate heat effectively. This keeps power losses and overheating to a minimum while increasing the system’s reliability, efficiency and lifespan. An optimally sized cross section can better handle fault conditions like short circuits and their associated damage.
- Regulatory Compliance: Because busbars handle high currents and voltages in critical applications, safety agencies and standards organizations have established regulations to ensure they operate as intended and also uphold the safety and reliability of their overall application. Busbars that carry UL listings meet the relevant standards for safely handling specified voltages and currents as well as being able to meet environmental criteria. Among UL standards, industrial busbars should comply with:
- UL 508A for Industrial Control Panels: UL 508A provides guidelines for industrial control panel construction as well as important components like busbars, defining aspects such as short-circuit ratings, insulation requirements and physical criteria such as mounting.
Engineers and facility managers may either select a UL-certified busbar or perform short-circuit tests on the unit. UL 508A also allows implementers to forgo short-circuit testing if the busbar system satisfies the requirements published in Table D3.1, which is part of UL 508A Annex D. This table covers critical ratings and characteristics pertaining to busbar widths, maximum short circuit current, maximum amperage ratings, voltage ratings (single or three-phases), distances between opposite-polarity busbars as well as distances between busbars when mounted face-to-face or edge-to-edge, and more. Table 3.1 is equivalent to UL 891 Table G3.1.
- UL 489 for Circuit Breaker Applications: Busbars are well-suited for use with circuit breakers, especially when deployed in control panels that house multiple circuit breakers. UL 489 sets requirements for a broad range of circuit breaker types, switches, enclosures and other devices that protect wires and cables from major electrical faults in low-voltage systems. The standard includes miniature circuit breakers (MCBs) whose compact size and resettability make them particularly attractive for use inside control panels.
When integrating a busbar with an MCB, look for a unit listed for use with UL 489 MCBs. This listing confirms that the busbar will withstand the faults that can occur in the intended control panel application. Also, make sure the busbar meets or exceeds the rated specifications and configurations of the MCB.
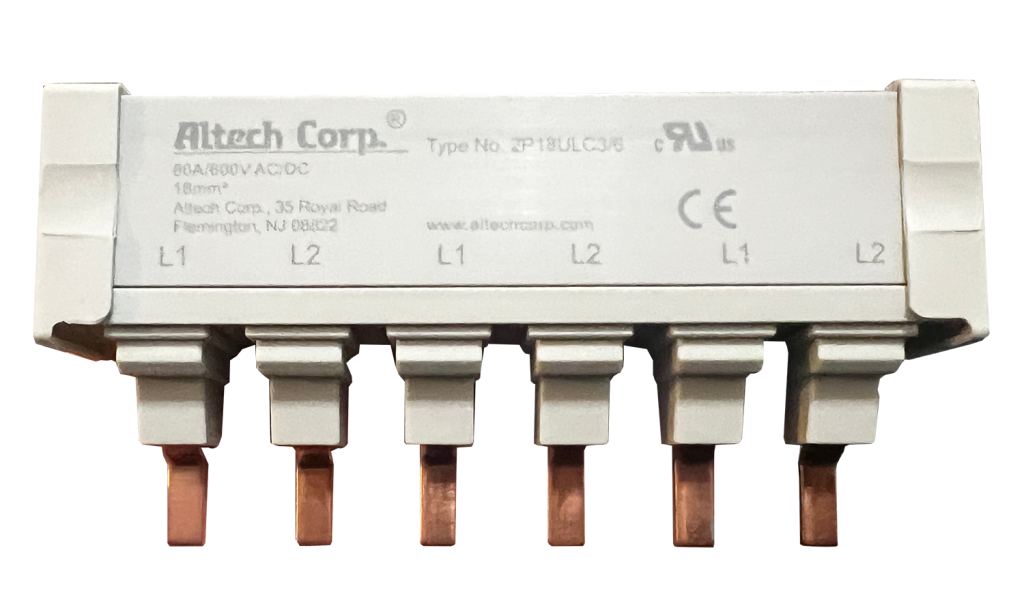
UL 489-compliant MCBs typically have a maximum line-rated current of 63A, although some MCBs are rated up to 115A for specific applications. Similarly, many MCBs are rated for 60 or 125V, but UL 489 covers higher voltages. Busbars come in single, double, and triple pole, with 6, 12, and 18 pins. Many UL 489 MCBs and busbars have separate accessories to make finger-safe terminals and end caps that keep installation and maintenance safe when working near energized components. Altech 489-listed busbars are rated to 115A/600V AC/DC.
Implementation Example:
A Strategy for Distribution Block Replacement
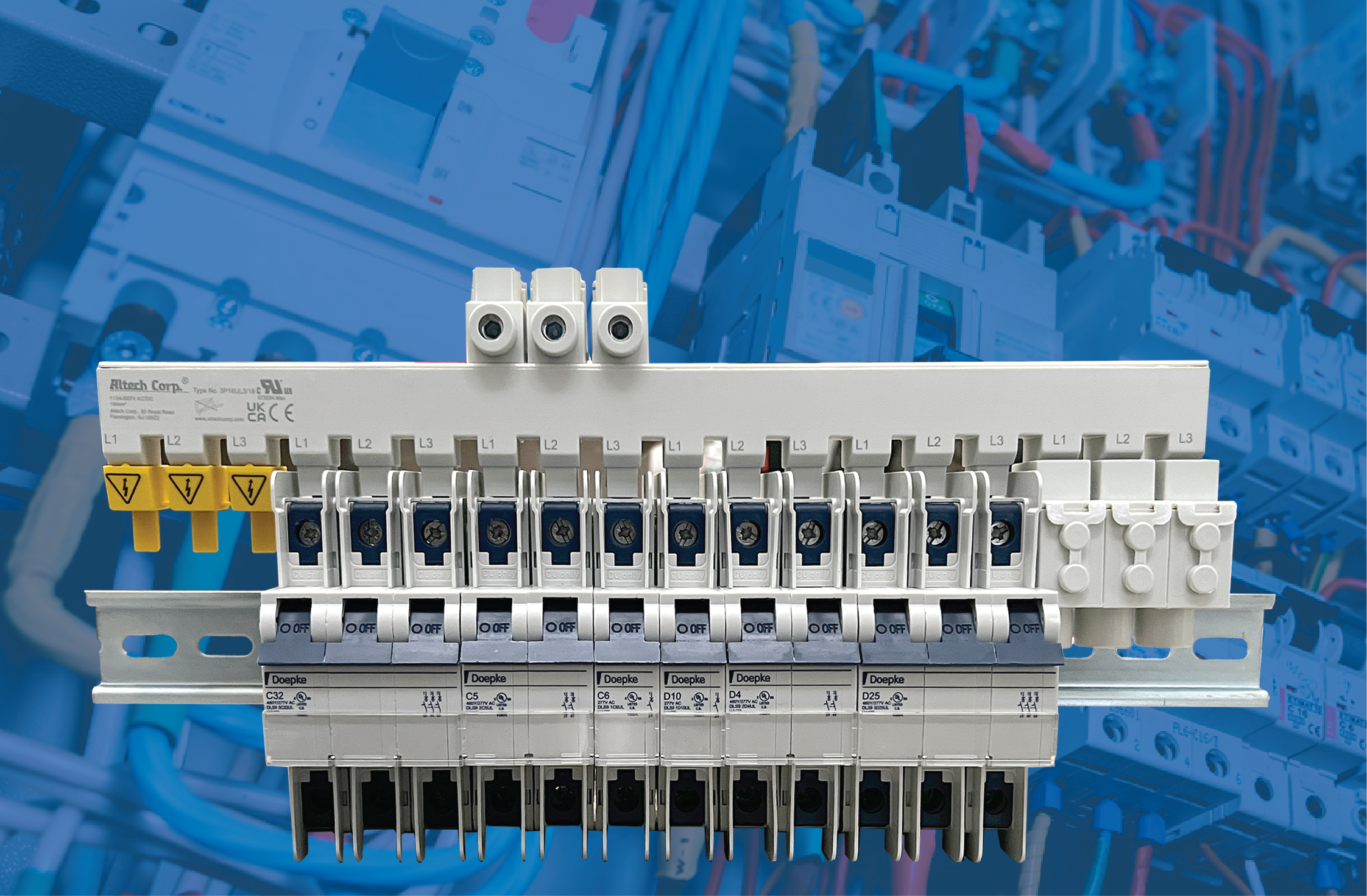
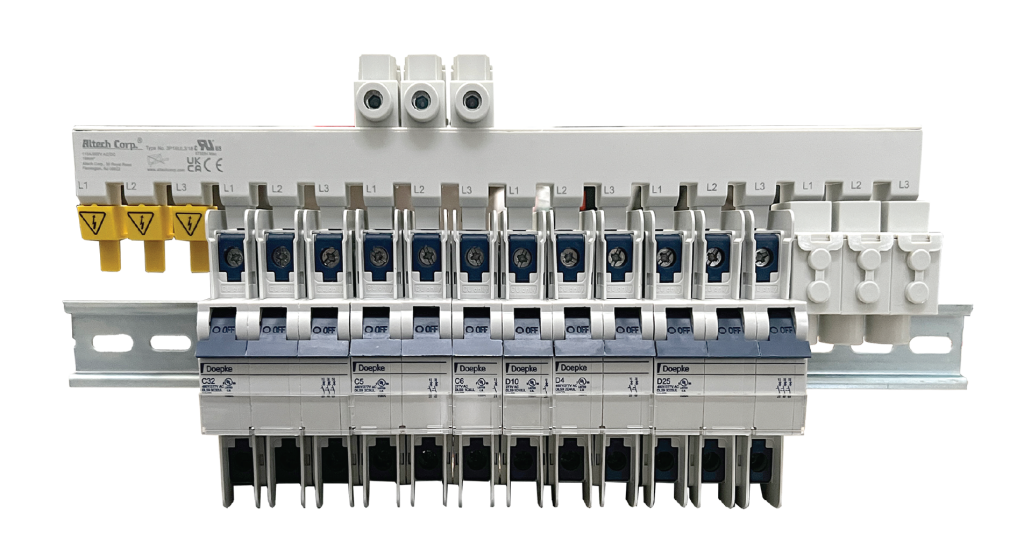
In industrial control panels where space is typically limited, distribution blocks tend to be bulky, and the wiring can consume even more space. Messy wiring makes troubleshooting and installation tedious and time-consuming. Busbars offer a much more compact design, freeing up panel space and allowing for easy expansion. Here is an example of a busbar that can streamline power distribution inside a control panel.
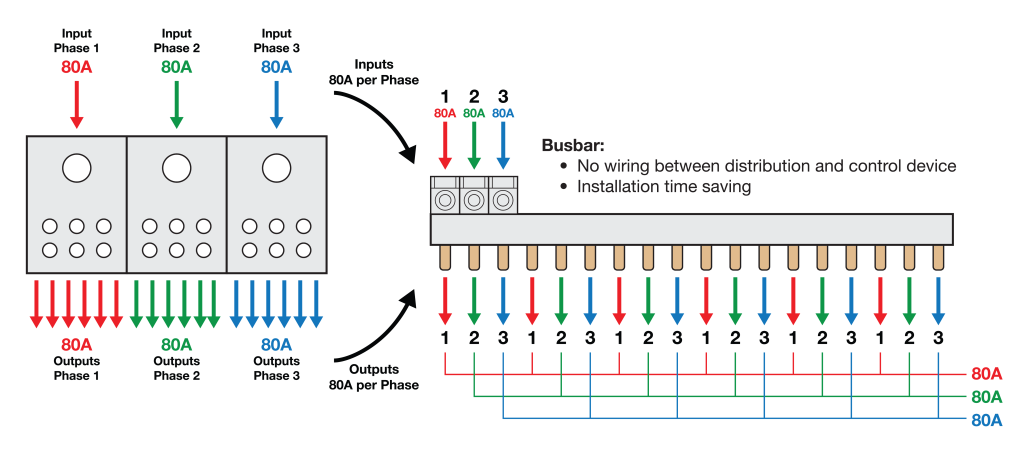
One popular distribution block is rated for 80A with one input and six outputs. To support the 80A inputs across three phases, a designer would need to add three units, each with its six 80-A outputs, side-by-side. However, a space-saving 3-phase 80A/480VAC 3P18U3/18 busbar for circuit breaker applications — part of the Altech 1077/508 Series — has an 18-pin, 6 x 3-pole configuration with mere 18 mm2 cross sections and a length of 315 millimeters (12.4 inches).
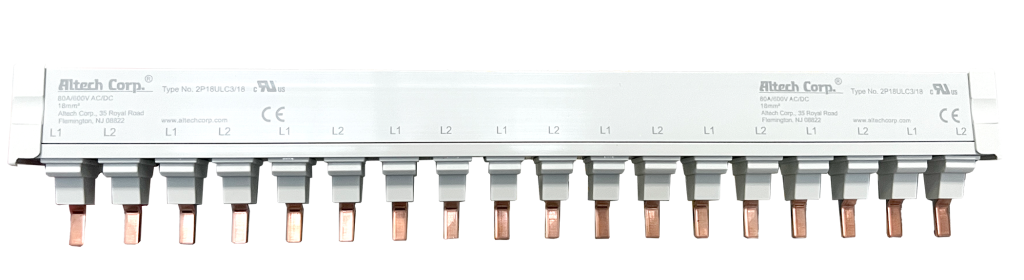
The 3P18U3/18 gives designers the flexibility to choose one of several pin configurations, and you can make a permanent connection to a power supply easily using an Altech 115A power feed lug, block or end device. Example configuration methods include:
- Start or end feed: Altech power feed lug P50UT or P50ULB and 18 mm2 (and 25 mm2) busbar (3P18(25)U3/18).
- Center or middle feed: Altech power feed lug P50UT and 18-mm2 busbar (3P18U3/18) rated to 115A.
- Center or middle feed: Altech power feed block P95UB and 18- and 25-mm2 busbar (3P(18)25U3/18). Accepts 160/200A input per phase.
Designed to jumper up to 57 poles of manual motor controllers (MMCs) and supplemental protectors (SPs), this busbar eliminates the wiring between the distribution and the control device, resulting in significant installation time savings.
Additionally, the copper construction of the 1077/508 Series makes the busbar less susceptible to loosening due to vibrations that often occur with conventional cable solutions in industrial environments.
Maximize Performance and Productivity
For many years, complex cabling systems and terminal blocks have been a tried-and-true method of power distribution in most industrial control box applications, and you can find many products from various vendors. However, the combined benefits of busbars systems — including cost-effectiveness, safety, space savings, optimal materials and adaptability — make them a compelling choice when high productivity and reliability are critical. When you select an innovative, UL-listed busbar system and leverage its benefits, configuration options and its many potential implementation possibilities, you’ll maximize your electrical system’s performance and your operation’s productivity.