Your Guide to Arc Flash Assessments

November 13, 2023
This webinar is a guide to understanding and mitigating the risks associated with arc flash. It provides a detailed exploration of the causes, potential hazards, and the critical importance of adhering to safety standards to protect personnel and equipment.
Speaker: Bill Brown, PE, CTO of US Consulting Services at Schneider Electric. Bill is an expert in electrical safety and specializes in providing advanced solutions to enhance workplace safety and improve electrical efficiency. Schneider Electric and Graybar are committed to delivering quality and innovative solutions to their clients, helping customers power, network, and secure their facilities with speed, intelligence, and efficiency.
This webinar is helpful for businesses and individuals operating in environments with complex electrical systems, especially those in industrial sectors. It is particularly beneficial for those in job roles that are responsible for maintaining electrical safety, risk management, and operational efficiency in their organizations.
Understanding Arc Flash Hazards:
Understanding the risks of arc flash is a critical aspect of electrical safety at your facility. It is crucial to comprehend the potential hazards and implement appropriate preventive measures to mitigate the risks associated with arc flash.
Arc flash occurs when there is a fault that causes an electric current to flow through an air gap between conductors, releasing energy in the form of light, heat, sound, and pressure. Arc flash can result in severe injuries, extensive equipment damage, and operational downtime. It can vaporize copper or aluminum, create hot plasma arc columns, and reach temperature levels usually associated with the sun.
Arc Flash Hazards:
- Intense Light and Heat: Arc flash can produce light and heat intense enough to cause severe burns and eye injuries.
- Pressure Wave: The rapid expansion of air creates a pressure wave capable of causing hearing damage and lung injury, and it can throw workers against walls or objects.
- Shrapnel: Molten metal and damaged equipment parts can be expelled at high velocity, posing a risk of injury.
- Toxic Gases: The superheated air can produce potentially harmful gases, which can be detrimental to respiratory health.
- Electrical Shock: Contact with energized components can result in electrical shock, leading to severe injuries or fatalities.
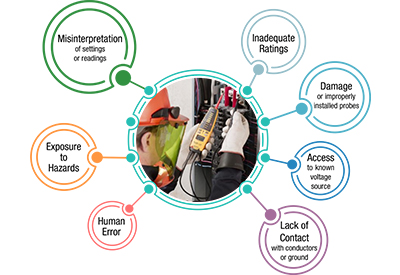
What Causes Arc Flash?
Arc flash can be caused by several factors, often related to equipment failure or human error. Here are some common causes of arc flash:
Equipment Failure:
- Aging Equipment: Over time, equipment can deteriorate, leading to an increased risk of arc flash incidents.
- Lack of Maintenance: Neglecting maintenance can result in equipment failures.
- Component Malfunction: Defective or malfunctioning components within electrical equipment can cause arc flash.
Human Error:
- Accidental Contact: Accidentally touching live components or causing a short circuit can trigger an arc flash.
- Improper Use of Tools: Using tools improperly or using damaged tools can cause faults leading to arc flash incidents.
- Working on Energized Equipment: Performing work on equipment that is energized increases the risk of arc flash.
Environmental Conditions:
- Dust and Debris: Accumulation of conductive dust and debris in electrical equipment can provide a path for electrical current, causing arc flash.
- Moisture: The presence of moisture can reduce the insulation resistance of electrical equipment, increasing the likelihood of arc flash.
- Corrosion: Corroded terminals and connections can increase electrical resistance and generate heat, potentially leading to arc flash incidents.
Other Issues:
- Incorrect Installation: Improperly installed equipment or components can lead to electrical faults and subsequent arc flash incidents.
- Overloaded Systems: Overloading electrical systems beyond their capacity can cause excessive heat and potential arc flash.
What is an Arc Flash Assessment?
For those wanting to mitigate arc flash hazards, it’s important to understand best practices, regulations, and the process for evaluating your facility’s risk. An Arc Flash Assessment is a systematic calculation of the arc-flash incident energy and arc-flash boundary at each piece of equipment included in the assessment.
What Are the Steps of An Arc Flash Assessment?
- Data Collection: For existing facilities, on-site data collection is important. Schneider will collect certain data like cable lengths, without requiring the opening of any devices or shutting down equipment. For new facilities, most, if not all, information can typically be obtained from drawings or cable take-offs from the electrical contractor. The duration of this step can vary from one day to several weeks, depending on the facility size.
- System Modeling: The collected data is used to model the system in software, such as ETAP, which is standard for Schneider Electric, although other packages can also be used if needed. This step involves running the analysis from the software to understand the potential risks and requirements for mitigating arc flash hazards.
- Analysis and Report Compilation: The results from the software analysis are tabulated, and a comprehensive report is compiled and delivered to the client, detailing the findings and recommendations from the arc flash assessment.
- Arc Flash Labeling: Optionally, arc flash labels and arc flash label affixing will be provided, as required on certain equipment by the National Electrical Code. These labels can give either a general hazard warning or specific information, such as calories per centimeter squared for selecting Personal Protective Equipment (PPE).
- Short Circuit and TCC Studies: Schneider will need to perform short circuit and time current coordination (TCC) studies as inputs to the arc flash assessment. Most of the data collected is to prepare for the short circuit and TCC components that feed into the arc flash assessment. Bundling these studies together with the arc flash assessment is generally recommended as it is usually less expensive.
Learn More About Arc Flash Assessment
Understanding and addressing arc flash hazards is crucial to maintaining a safe working environment, preventing accidents, and ensuring the well-being of your employees. By implementing proper safety protocols and procedures, businesses can significantly reduce the risks associated with arc flash and protect their workforce and equipment from potential harm.